

Next: Examples
Up: The Fitter Handbook
Previous: Installation
Subsections
Fitter is a C++ program aimed to fit a chosen theoretical
multi-parameter function through a set of data points.
The method of fitting is chi-square minimization.
Moreover, the robust fitting method can be applied in Fitter.
Fitter was designed to be used for a small-angle neutron
scattering data analysis.
Respective theoretical models are implemented in it.
Some commonly used models (Gaussian and polynomials) are also
implemented for wider applicability.
fitter
-{ std sans
sans yumo} model
[-s name]
[-r]
[-R x1:x2]
[-v[ file]]
[-o file]
[-H file]
[-rc-read]
[-rc-write]
file
yumo} model
[-s name]
[-r]
[-R x1:x2]
[-v[ file]]
[-o file]
[-H file]
[-rc-read]
[-rc-write]
file
fitter
[-h]
[-V]
Input data file (ASCII) for fitter should have at least three columns:
the first one would be interpreted by fitter as "X"-samples,
second one - as "Y"-samples and the third one - as "Y"-errors.
For YuMO models (see below) should be one more column, which is interpreted
as "X"-errors.
- -std model
- Standard models. One of the following (see '-std help' for list):
- g
- Gaussian
- e
- Exponential
- p0
- Polynomial of the order 0
- p1
- Polynomial of the order 1
- p2
- Polynomial of the order 2
- p3
- Polynomial of the order 3
- p4
- Polynomial of the order 4
- p5
- Polynomial of the order 5
- p6
- Polynomial of the order 6
- p7
- Polynomial of the order 7
- p8
- Polynomial of the order 8
- -sans model
- SANS models. One of the following (see '-sans help' for list):
- b
- Ball
- c
- Cylinder
- c2
- Elliptical cylinder
- e2
- Two axis ellipsoid
- p
- Parallelepiped
- ss
- Spherical shell
- -yumo model
- SANS models for YuMO spectrometer.
One of the following (see '-yumo help' for list):
- b
- Ball with resolution
- c
- Cylinder with resolution
- c2
- Elliptical cylinder with resolution
- e2
- Two axis ellipsoid with resolution
- p
- Parallelepiped with resolution
- ss
- Spherical shell with resolution
- -s, -strategy name
- Change MINUIT strategy. MINIMIZE is a default one.
- -r, -robust
- Robust fitting. Useful for highly noised data.
- -R, -range x1:x2
- Fitting in range from x1 to x2.
Note that no fit is applied if a range appearers to be empty.
- -v, -verbose[ file]
- Output MINUIT processing information.
No output is produced by default.
Repeating this option determines how much output will be produced:
- minimum MINUIT output
- normal MINUIT output
- additional output giving intermediate results
- maximum output, showing progress of minimizations
- -o, -output file
- Output data file with the resulting theoretical curve.
No file is created by default.
- -H, -header file
- Output resulting parameters and chi-square value to file
(standard output by default).
File may be the same as for theoretical curve, parameters and chi-square
will be put to its beginning in this case.
- -rc-read
- Read rc-file.
If specified, this option cause reading parameters staring values from
rc-file.
Some times this can highly speed-up minimization.
Rc-file .fitter should exist in $HOME (in C: on Windows).
- -rc-write
- Write rc-file.
If specified, this option cause writing resulting parameters to rc-file.
Useful for creating/repairing rc-file.
Rc-file .fitter is placed in $HOME (in C: on Windows).
- -h, -help
- Display short help message and exit.
- -V, -version
- Display version information and exit.
Fig. 2:
Fitter's main window
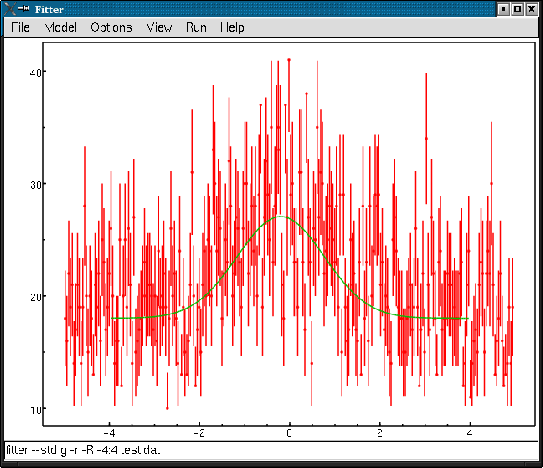 |
Besides the command-line interface the Fitter offers an user friendly GUI
(graphical user interface).
Fitter's main window, shown in fig.2, is implemented in the
standard manner with menu-bar, tool-bar and status-bar.
All menu items exactly correspond to the command-line options described above.
The command-line to be executed is just formed by choosing corresponding menu
items and is displayed on the status-bar.
Some of the most frequently used menu items are duplicated as buttons or
combo-boxes on the tool-bar.
A window with fitting results arises after fit is complete.


Next: Examples
Up: The Fitter Handbook
Previous: Installation
Alexei Soloviev
2008-01-20
![]() sans
sans![]() yumo} model
[-s name]
[-r]
[-R x1:x2]
[-v[ file]]
[-o file]
[-H file]
[-rc-read]
[-rc-write]
file
yumo} model
[-s name]
[-r]
[-R x1:x2]
[-v[ file]]
[-o file]
[-H file]
[-rc-read]
[-rc-write]
file